HRB publishes 2024 psychiatric inpatient figures
10 Jul 2025 - 3 min read

10 Jul 2025 - 3 min read

26 Jun 2025 - 5 min read

26 Jun 2025 - 6 min read

11 Jun 2025 - 4 min read

30 May 2025 - 3 min read

12 May 2025 - 1 min read

8 May 2025 - 2 min read

27 Feb 2025 - 1 min read
25 Feb 2025 - 2 min read

30 Jan 2025 - 3 min read

22 Jan 2025 - 2 min read
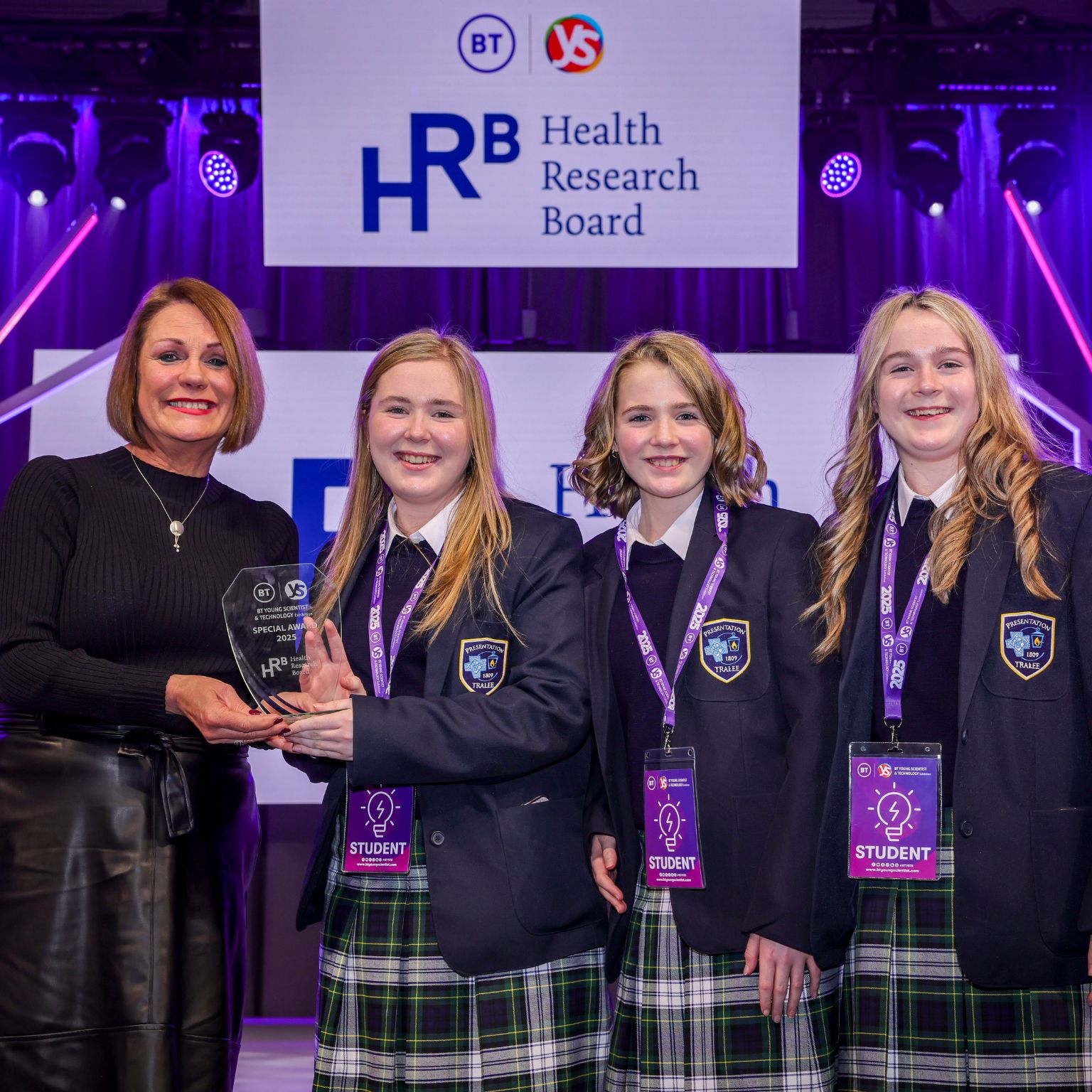

15 Jan 2025 - 2 min read

20 Dec 2024 - 3 min read

18 Dec 2024 - 3 min read
18 Dec 2024 - 2 min read

17 Dec 2024 - 2 min read
17 Dec 2024 - 4 min read

17 Dec 2024 - 4 min read

10 Dec 2024 - 3 min read
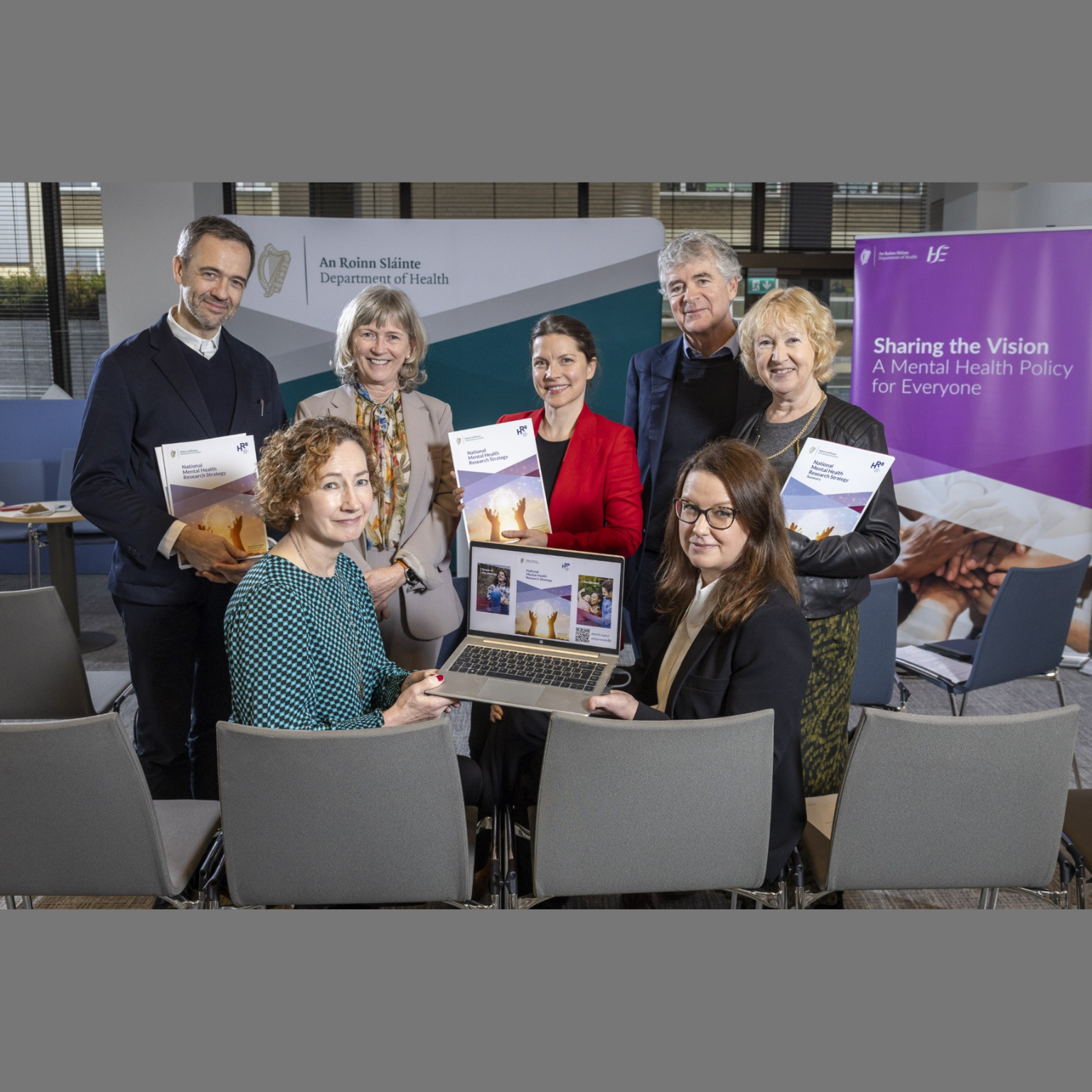

4 Dec 2024 - 3 min read

28 Nov 2024 - 3 min read

26 Nov 2024 - 3 min read

26 Nov 2024 - 3 min read

21 Nov 2024 - 2 min read
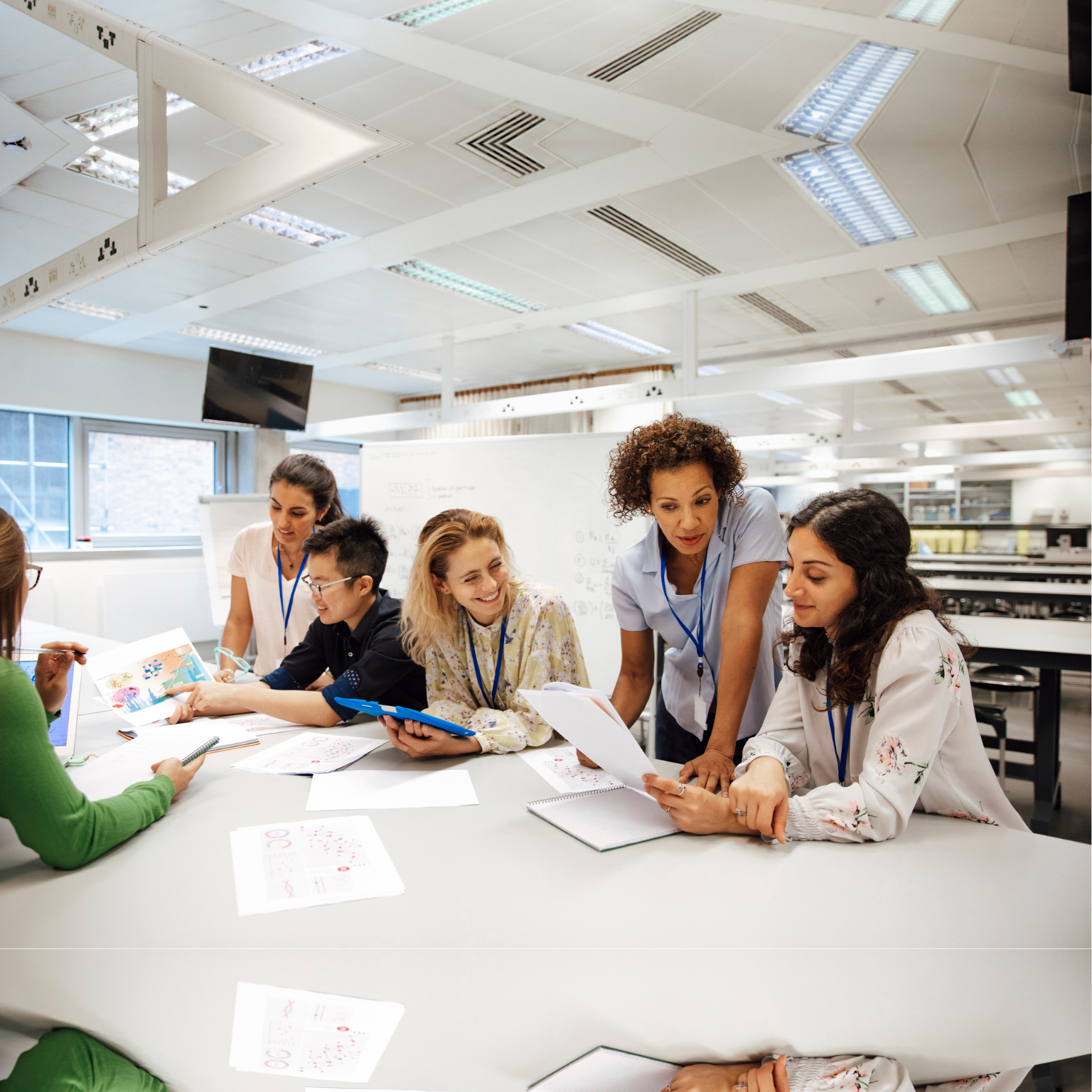

5 Nov 2024 - 5 min read

Displaying 1 - 25 of 579 results